My issue has been solved too 
I have released a new version of the required packages to test the infinite scroll hook:
@frontity/hooks@2.1.0-infinite-scroll-beta.4@frontity/tiny-router@1.3.2-infinite-scroll-beta.0@frontity/wp-source@1.10.1-infinite-scroll-beta.0
 Hey! Some updates here:
Hey! Some updates here:
The PR (#652) where we’ve been preparing the infinite scroll hooks to be officialy released is almost done. I’ll be working on writing the Final Implementation post in the meantime. Just so you know, the API will remain the same.
Keep tuned! 
Pull Request
Requirements
Feature:
-
@frontity/hooks(^2.2.0)
Dependencies:
-
@frontity/tiny-router(to be filled once the latest version is released) -
@frontity/wp-source(to be filled once the latest version is released)
Functionalities
Three React hooks were implemented. Two for general use:
useArchiveInfiniteScrollusePostTypeInfiniteScroll
And a basic one for implementing custom infinite scroll hooks (used internally
by the previous two hooks):
useInfiniteScroll
NOTE:
useInfiniteScrollis not intented to be used directly by theme
developers unless they are creating their own infinite scroll logic.
The main idea behind these hooks is that they return a list of Wrapper
components, one for each entity listed while scrolling, that handle both the
route updating and fetching of the next entity.
Also, the following action was added to the @frontity/router API and the
@frontity/tiny-router package.
-
actions.router.updateState- Function to update the content of the browser
history state for the current link.
Infinite scroll hooks
useInfiniteScroll
This is the core hook with the basic logic to build an infinite scroll hook.
It basically receives two links, currentLink and nextLink, and returns two
React refs that should be attached to react elements. The hook uses useInView
internally to track the visibility of those elements and trigger an
actions.router.set to update the current link or an actions.source.fetch to
fetch the next entity. You can pass options for these useInView hooks as well,
using the fetchInViewOptions and the routeInViewOptions params.
useInfiniteScroll also keeps a record of the fetched & ready entities in the
browser history state, in order to restore the list when you go back and
forward while navigating. That record is accessible from the browser history
state under the infiniteScroll.links array.
Note: the history state is also accessible from the Frontity state, in
state.router.state.
It was designed to be used inside a Wrapper component that would wrap the
entity pointed by currentLink.
Parameters
It requires an object with the following props:
| Name | Type | Default | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
currentLink |
string | - | yes | The current link that should be used to start the infinite scroll. |
nextLink |
string | - | no | The next link that should be fetched and loaded once the user scrolls down. |
fetchInViewOptions |
IntersectionOptions | - | no | The intersection observer options for fetching. |
routeInViewOptions |
IntersectionOptions | - | no | The intersection observer options for routing. |
NOTE: The IntersectionOptions type refers to the type of the the parameters
received by theuseInViewhook.
Return value
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
supported |
boolean | Boolean indicating if the Intersection Observer is supported or not by the browser. |
routeRef |
React.Ref | The ref that should be attached to the element used to trigger actions.router.set. |
fetchRef |
React.Ref | The ref that should be attached to the element used to trigger actions.source.fetch. |
routeInView |
boolean | Boolean that indicates when the element used to trigger actions.router.set is in the screen. |
fetchInView |
boolean | Boolean that indicates when the element used to trigger actions.source.fetch is in the screen. |
Usage
Note: this is just an example to illustrate how the
useInfiniteScrollworks.
For better examples, see theuseArchiveInfiniteScrolland the
usePostTypeInfiniteScrollimplementation.
import { useConnect, connect, css } from "frontity";
import useInfiniteScroll from "../use-infinite-scroll";
import { isArchive, isError } from "@frontity/source";
export const wrapperGenerator = ({
link,
fetchInViewOptions,
routeInViewOptions,
}) => {
const Wrapper = ({ children }) => {
const { state } = useConnect();
const current = state.source.get(link);
const next =
isArchive(current) && current.next
? state.source.get(current.next)
: null;
const { supported, fetchRef, routeRef } = useInfiniteScroll({
currentLink: link,
nextLink: next?.link,
fetchInViewOptions,
routeInViewOptions,
});
if (!current.isReady || isError(current)) return null;
if (!supported) return children;
const container = css`
position: relative;
`;
const fetcher = css`
position: absolute;
width: 100%;
bottom: 0;
`;
return (
<div css={container} ref={routeRef}>
{children}
{<div css={fetcher} ref={fetchRef} />}
</div>
);
};
return connect(Wrapper);
};
useArchiveInfiniteScroll
This hook implements the logic needed to include infinite scroll in archives
(i.e. categories, tags, the posts archive, etc.).
The hook receives options to set a limit of pages shown automatically, to
disable it, and also settings for the intersection observers that are passed to
the useInfiniteScroll hooks used internally.
useArchiveInfiniteScroll is designed to be used inside an Archive component.
That component would render all the archive pages from the pages returned by the
hook.
Apart from that list, it returns a set of boolean values to know if the next
pages is being fetched, if the limit has been reached or if the next page
returned an error, and a function to fetch the next page manually.
Parameters
It accepts an optional object with the following props:
| Name | Type | Default | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
active |
boolean | true |
no | A boolean indicating if this hook should be active or not. It can be useful in situations where users want to share the same component for different types of Archives, but avoid doing infinite scroll in some of them. |
limit |
number | infinite |
no | The number of pages that the hook should load automatically before switching to manual fetching. |
fetchInViewOptions |
IntersectionOptions | - | no | The intersection observer options for fetching. |
routeInViewOptions |
IntersectionOptions | - | no | The intersection observer options for routing. |
NOTE: The IntersectionOptions type refers to the type of the the parameters
received by theuseInViewhook.
Return value
An object with the following properties:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
pages |
Array of page props | An array of the existing pages. Users should iterate over this array in their own layout. The content of each element of this array is explained below. |
isFetching |
boolean | If it’s fetching the next page. Useful to add a loader. |
isLimit |
boolean | If it has reached the limit of pages and it should switch to manual mode. |
isError |
boolean | If the next page returned an error. Useful to try again. |
fetchNext |
function | A function that fetches the next page. Useful when the limit has been reached (isLimit === true) and the user pushes a button to get the next page or when there has been an error fetching the last page and the user wants to retry. |
Each element of the pages array has the following structure:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
key |
string | A unique key to be used in the iteration. |
link |
string | The link of this page. |
isLast |
boolean | If this page is the last page. Useful to add separators between pages, but avoid adding it for the last one. |
Wrapper |
React.FC | The Wrapper component that should wrap the real Archive component. |
Usage
import { connect, useConnect } from "frontity";
import { useArchiveInfiniteScroll } from "@frontity/hooks";
import ArchivePage from "./archive-page";
/**
* Simple component showing the usage of the `useArchiveInfiniteScroll` hook.
*
* @example
* ```
* // In the Theme component:
* <Switch>
* {...}
* <Archive when={data.isArchive} />
* </Switch>
* ```
*/
const Archive = () => {
// Get the list of pages from the hook.
const {
pages,
isFetching,
isLimit,
isError,
fetchNext,
} = useArchiveInfiniteScroll({ limit: 3 });
return (
<>
{pages.map(({ Wrapper, key, link, isLast }) => (
<Wrapper key={key}>
<ArchivePage link={link} />
{!isLast && <PageSeparator />}
</Wrapper>
))}
{isFetching && <div>Loading more...</div>}
{(isLimit || isError) && (
<button onClick={fetchNext}>
{isError ? "Something failed - Retry" : "Load More"}
</button>
)}
</>
);
};
export default connect(Archive);
usePostTypeInfiniteScroll
Hook that implements the logic needed to include infinite scroll in a post type
view (i.e. posts, pages, galleries, etc.).
This hook is more complex than the previous one, as it works getting the post
type entities from the specified archive and thus it doesn’t fetch the next post
but the next page of posts.
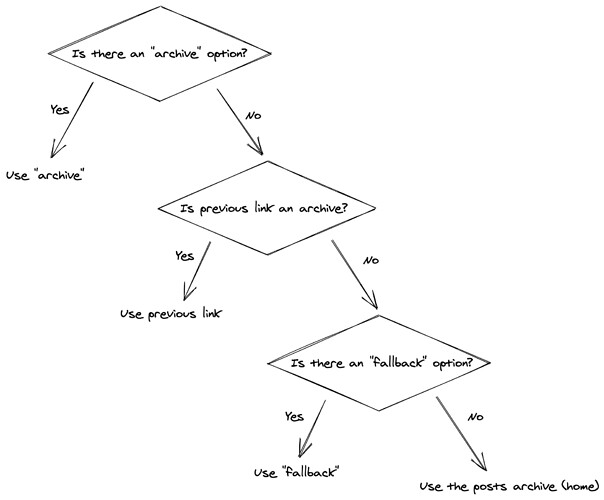
It recevies an archive and a fallback prop ―both links―, to specify the
source of the post entities. If none of them is specified,
state.source.postsPage is used. When the penultimate post of the first page is
rendered, the next page of the archive is fetched. A list of the fetched pages
is stored in the browser history state along with the list of posts.
The limit prop in this case stands for the number of posts being shown, not
the number of fetched pages. In the same way, the fetchNext shows the next
post, and only fetches the next page of posts if needed.
Parameters
It accepts an optional object with the following props:
| Name | Type | Default | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
active |
boolean | true |
no | A boolean indicating if this hook should be active or not. It can be useful in situations where users want to share the same component for different types of Archives, but avoid doing infinite scroll in some of them. |
limit |
number | infinite |
no | The number of pages that the hook should load automatically before switching to manual fetching. |
archive |
string | - | no | The archive that should be used to get the next posts. If none is present, the previous link is used. If the previous link is not an archive, the homepage is used. |
fallback |
string | - | no | The archive that should be used if the archive option is not present and the previous link is not an archive. |
fetchInViewOptions |
IntersectionOptions | - | no | The intersection observer options for fetching. |
routeInViewOptions |
IntersectionOptions | - | no | The intersection observer options for routing. |
NOTE: The IntersectionOptions type refers to the type of the the parameters
received by theuseInViewhook.
Return value
The output of these hooks is pretty similar to the previous one’s:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
posts |
Array of post props | An array of the existing posts. Users should iterate over this array in their own layout. The content of each element of this array is explained below. |
isFetching |
boolean | If it’s fetching the next post. Useful to add a loader. |
isLimit |
boolean | If it has reached the limit of posts and it should switch to manual mode. |
isError |
boolean | If the next page returned an error. Useful to try again. |
fetchNext |
function | A function that fetches the next post. Useful when the limit has been reached (isLimit === true) and the user pushes a button to get the next post or when there has been an error fetching the last post and the user wants to retry. |
Each element of the posts array has the following structure:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
key |
string | A unique key to be used in the iteration. |
link |
string | The link of this page. |
isLast |
boolean | If this post is the last post. Useful to add separators between posts, but avoid adding it for the last one. |
Wrapper |
React.FC | The Wrapper component that should wrap the real Post component. |
Usage
import { connect, useConnect } from "frontity";
import { usePostTypeInfiniteScroll } from "@frontity/hooks";
import PostTypeEntity from "./post-type-entity";
/**
* Simple component showing the usage of the `usePostTypeInfiniteScroll` hook.
*
* @example
* ```
* // In the Theme component:
* <Switch>
* {...}
* <PostType when={data.isPostType} />
* </Switch>
* ```
*/
const PostType = () => {
// Get the list of posts from the hook.
const {
posts,
isFetching,
isLimit,
isError,
fetchNext,
} = usePostTypeInfiniteScroll({ limit: 5 });
return (
<>
{posts.map(({ Wrapper, key, link, isLast }) => (
<Wrapper key={key}>
<PostTypeEntity link={link} />
{!isLast && <PostSeparator />}
</Wrapper>
))}
{isFetching && <div>Loading more...</div>}
{(isLimit || isError) && (
<button onClick={fetchNext}>
{isError ? "Something failed - Retry" : "Load More"}
</button>
)}
</>
);
};
export default connect(PostType);
More things added
actions.source.updateState
Action that replaces the value of state.router.state with the give object. The
same object is stored in the browser history state using the
history.replaceState()
function.
Parameters
| Name | Type | Default | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
historyState |
object | - | yes | The object to set as the history state. |
Out of Scope
I was out of the scope of this PR to implement a way to let developers to change
the logic that usePostTypeInfiniteScroll uses to get the next post.
Right now, that logic is the following:
- If the post is the first post rendered and it’s not included in the first page
of the archive, the next post is the first post of the archive. - For any other case, get the index where the post appears in the fetched pages.
The next post will be the one with index + 1.
API changes
Backward compatible changes
Instead of having to import each hook from its module, hooks can be imported now
from the package root:
import { useInView, useInfiniteScroll } from "@frontity/hooks";
They can still be imported directly from each module:
import useInView from "@frontity/hooks/use-in-view";
import useInfiniteScroll from "@frontity/hooks/use-infnite-scroll";
Breaking changes
No breaking changes.
Deprecated APIs
No deprecated APIs.
Technical explanation
Work in progress.
I said so in the PR, but I’ll repeat it here.
I don’t have words to say how amazing this feature is guys. This implementation is simply brilliant. And the test coverage is outstanding.
It is the best infinite-scroll feature a frontend framework could dream of:
- 100% of abstraction of the infinite scroll logic.
- 100% of control of the layout to the developer.
Congratulations to both @orballo and @david for your amazing work 


BRAVO! 

I’ve just read the FI. Great work, thanks @david 
I’ve added isLimit and fetchNext to the examples to show how to use them, can you review them and let me know if they are correct?
Also, the logic behind the "archive" and "fallback" is a bit difficult to understand so I did this drawing:
Can you review it and confirm that is correct? (link to the excalidraw)
Thanks!
@David I’ve seen that there isn’t yet a issue in the docs repo for this. Could you please create it and link it to the Final Implementation?
You’re right, thanks for the reminder. 
EDIT: issue created Document the Infinite Scroll hooks · Issue #14 · frontity/api-reference · GitHub
They are correct. The only thing is that isLimit and isError could be true at the same time, so you could end up having two buttons for fetching the next element. 
Yup, is correct. 
Interesting 
What about this:
const PostType = () => {
// Get the list of posts from the hook.
const {
posts,
isFetching,
isLimit,
isError,
fetchNext,
} = usePostTypeInfiniteScroll({ limit: 5 });
return (
<>
{posts.map(({ Wrapper, key, link, isLast }) => (
<Wrapper key={key}>
<PostTypeEntity link={link} />
{!isLast && <PostSeparator />}
</Wrapper>
))}
{isFetching && <div>Loading more...</div>}
{(isLimit || isError) && (
<button onClick={fetchNext}>
{isError ? "Something failed - Retry" : "Load More"}
</button>
)}
</>
);
};
Yes, I think that way is better. 
Ok, I’ve changed it in your FI 
This feature has been released ![]() : Read the full Release Announcement.
: Read the full Release Announcement.
I’ve created a demo to show how it works and how to implement it:
And this is the CodeSandbox with the code used → xenodochial-sanderson-0rieb - CodeSandbox
Hi,
I think I found a bug in the Infinite Scroll hook.
Even in the sandbox that @SantosGuillamot sent in the last comment this bug is present.
When you scroll/click to load more items the URL will be updated, eg /page/2/.
Great feature, works perfectly, but - if you will refresh the page - previous pages will disappear and the list with items will start from the page you have in the URL.
So if user wants to copy the URL/save it somewhere and come back to this page later or even just refresh the page he will never see any items from previous pages.
Is there any workaround for this issue?
Hi @marek !
You’re right that in the demo it isn’t possible to navigate to the previous page if you go directly to /page/2/, but I am not sure if it is a bug. I think it’s just an issue with how the theme in the demo is created. I removed the pagination because I thought it didn’t make sense with the Infinite Scroll, but if anyone wants it in the list, I guess it should be as simple to add this code again. For example, you could import it below the navigation or wherever you want. Something like this:
...
import Pagination from "./pagination";
const List = () => {
const {
pages,
isLimit,
isFetching,
isError,
fetchNext
} = useArchiveInfiniteScroll({ limit: 3 });
return (
<>
<Pagination />
{pages.map(({ key, link, isLast, Wrapper }) => (
<Wrapper key={key}>
<ListPage link={link} />
{!isLast && <hr />}
</Wrapper>
))}
<ButtonContainer>
{isFetching && <Loading />}
{isLimit && <Button onClick={fetchNext}>Load Next Page</Button>}
{isError && (
<Button onClick={fetchNext}>Something failed - Retry</Button>
)}
</ButtonContainer>
</>
);
};
export default connect(List);
Adding the pagination is not really an option.
If we have a design with infinite scroll we don’t want to have pagination. So it’s not an option to add a pagination just because the plugin doesn’t support basic features like going back to previous page or at least disable url on load more to prevent this behavior.
How can anyone meet design with infinite scroll if he have to add normal pagination to make sure user can go back to previous page?
I am afraid that the feature that you are requesting is not possible to implement by default. Once you refresh the page, the state is lost, therefore there is no way for the infinite scroll to know what was loaded before. And we cannot asume that if the user is on page 2, he wants to load all the previous pages just by default, because the user could also be in page 345, and that behaviour would be probably not desired.
You may be able to implement on your own a way to fetch those pages automatically when the list is not loaded in the first page if that is the behaviour you actually want.
Yes, but it would be much easier if your plugin expose some functions to do that, eg. fetchPrev similar to fetchNext.
Let’s say I want to add a button which will load the previous page. It should be visible only if user directly loaded other page than the first one. To do it I need to basically repeat the whole logic of your plugin, but in other direction - not fetching next, but previous page.
Within Frontity you already have the previous page, since it’s still available from when you were there.
Unless you hard refresh the page, at which point you also don’t know what the previous page was.
Using an internal pagination is actually the only solution. This way both the URI and state of each page gets stored, and even when someone would go there from an external source or hard refresh, it would still load the “current” results.
Only interesting design choice would be, how to handle scrolling upwards?